Collaboration between two adjacent components, multiple components work as a whole.The purpose is to Avoid consuming ATP produced by glucose to produce glucose. Perhaps there should be other methods.
edit:
I went to further understand the evolution of photosynthesis.
It seems that the energy supply and hydrogen source decomposition should be integrated into one structure, Hydrogen source decomposition exists as an upgrade of structure.
One possible solution is that the energy supply structure upgraded with hydrogen source decomposition function not only generates ATP but also NADPH, which are required for glucose synthesis. The amount of NADPH will limit the ATP used for glucose synthesis within its autotrophic capacity range.
This design is not only applicable for photosynthesis, but also compatible with chemoautotrophic effects. The existence of Photoelectric autophy and Carboxysome means it has realism.
Carboxysome
Carboxysome is the unique inclusion body structure of autotrophic bacteria, which exists in chemoautotrophic Thiobacillus, Beggiatoa and some photoautotrophic cyanobacteria.
Photoelectric autophy may be that life began to try to use light energy, while life may have directly used hydrogen gas for carbon dioxide fixation earlier on. The Wood Ljungdahl pathway is widely present in anaerobic bacteria and archaea.
If Photoelectric autophy is considered, rutile can be added as a new rock to provide photoelectrons for surrounding cells under light, and new extracellular structures can be added to convert photoelectrons into NADPH and ATP.
Taking the Optical System as an Example (Pigment Evolution Route)
porphyrin [free] (Adaptive radiation, light ATP generation)→bacteriochlorophyll [photosynthetic membrane] (Adaptive radiation, light ATP generation, hydrogen source: hydrogen sulfide)→chlorophyll [thylakoid] (Adaptive radiation, light ATP generation, hydrogen source: hydrogen sulfide, water{ Oxygen production})
Carotene [free] (Adaptive radiation, Weak light ATP generation)→Retinal [photosynthetic membrane] (Adaptive radiation,Strong light ATP generation, hydrogen source: hydrogen sulfide)
Eumelanin [vacuole] (Extreme radiation adaptation)→Allomelanin[vacuole] (Extreme radiation adaptation, high radiation ATP generation, hydrogen source: water)
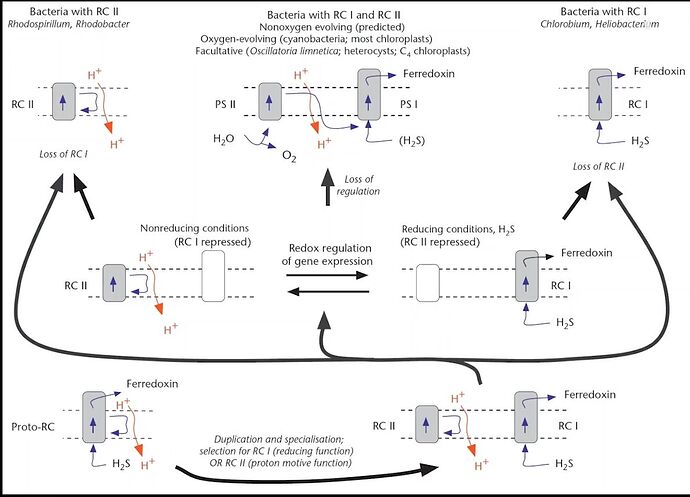
Evolution of photosystem
RC 1: reducing fuction, producing NADPH
RC 2: proton motive fuction, producing ATP, (Water decomposition, from OEC)
Heliobacteria was found to have a relatively primitive single photoreaction center.
I have found some information about oxygen evolution complexes (OECs), which are the only protein complexes in nature that can decompose water at ordinary temperature.
If passive protease is implemented, it can be used as an unlocking condition for oxygen production photosynthesis.
It is worth mentioning that Nitrosopululus maritimus has the ability to produce oxygen without the need for light, although the production is only sufficient for their own use.
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abe6733
edit:
I searched for some information about Photoheterotroph. Photoheterotroph is not incapable of producing glucose, it still has the ability to utilize RuBisCO to fix CO2. Organic matter is more important as a hydrogen source for it. From this perspective, various production methods can have a direct mode of producing NADPH before utilizing H2S and H2O (organic matter cycle).